[This essay was published in The Cairo Review in December 2016.]
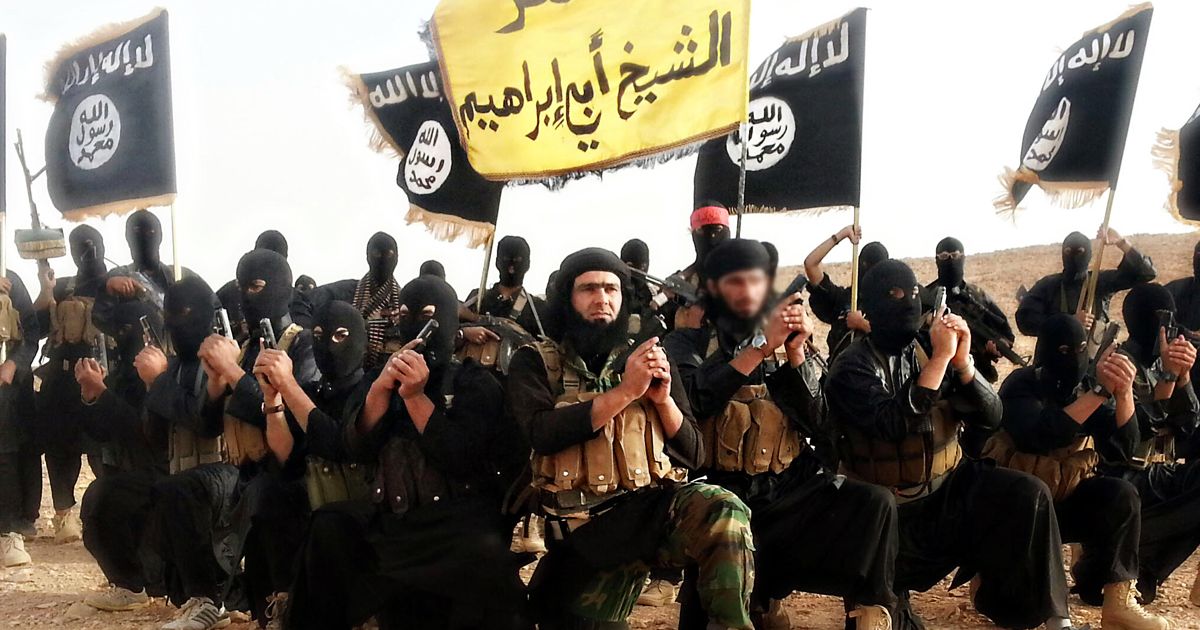
Almost daily its beleaguered leaders of the Islamic State group (commonly known by the acronym ISIS) receive bad news. It is rapidly losing territory. After the fall of Fallujah and Ramadi, the city of Mosul is next on the target of government forces in Iraq, and in Syria the de facto ISIS capital of Raqqa is increasingly under siege. In the northern part of Syria and Iraq, from Kobani to the strategic town of Sinjar, the region has been liberated by Kurdish forces. The vast territorial reach of ISIS in 2015 that encompassed much of eastern Syria and western Iraq has shrunk to a smaller network of outposts with the intervening landscape under questionable control.
Moreover it is losing support both within and outside its territory of control. Military strikes from the United States military and its coalition, along with Russian efforts, have crippled the movement’s transportation infrastructure and economic power. The numbers of foreign volunteers have dwindled, in part because they have been killed off in military encounters, in suicide attacks, and by missile strikes. Two of their most famous recruits, notorious around the world for beheading ISIS captives, have themselves been killed by targeted strikes. Scores, perhaps hundreds, have been trying to return home, the men weary of being used as cannon fodder, the women desperate from being used as sex slaves.
The terrorist attacks in Istanbul, Paris and Brussels have been meant to contradict this bad publicity, to portray an illusion of power. The acts were intended to bolster the morale of the ISIS stalwarts and to show potential young Muslim volunteers from around the world that it is still capable of making a global impact. Yet ISIS, it appears, is on a downward slide.
How, then, will ISIS end? And what will come in its place? To answer these questions we have to look at what ISIS is—not just one movement but at least three different sorts of groups in an uneasy coalition, each with its own agenda and its own possibilities for long-term continuity even after the fall of ISIS’ territorial claims. ISIS is simultaneously a movement for Sunni Muslim empowerment, a global jihadi movement, and an apocalyptic cult. Each of these groups may be around in one form or another long after the roads from Baghdad to Mosul and from Damascus to Raqqa have been secured.
ISIS as Sunni Empowerment
Though ISIS seemed to come out of nowhere its territorial claims were very specific: the Arab Sunni heartland of eastern Syria and western Iraq. Before the leaders of the movement shortened its name to “the Islamic State” (or “Caliphate”) it called itself al-Dawla al-Islamiya al-Iraq al-Sham, an Arabic phrase that can be translated into English as “the Islamic State of Iraq and Greater Syria.” The term al-Sham, or “greater Syria,” includes the present nation states of Syria, Lebanon, Jordan and Israel, the region that the French called “the Levant” which is why its initials in English are sometimes given as ISIL rather than ISIS. It is also called “Da’ish or Daesh,” a word that based on the acronym for the Arabic name for the movement. By coincidence, in Arabic the term daesh also means something like the word for “bullies,” and for that reason ISIS leaders are annoyed by its usage. Probably also for that reason the term persists among those victimized by it.
Though newly empowered in 2014, the origins of the movement date back to the social unrest that developed in Iraq after the invasion and occupation by coalition troops led by the United States military in 2003. At that time the overthrow of the Iraqi dictator, Saddam Hussein, was greeted by a certain degree of apprehension within al Anbar province and other areas of western Iraq where Arab Sunni Muslim communities dominated. When I spoke with Sunni leaders from al Anbar province in Iraq in 2004, they told me that they did not mourn the loss of Saddam Hussein, but what they feared was the loss of Sunni power. Even though Saddam’s rule was secular it had favored his own minority Sunni community. In the post-Saddam Iraq the Shi’a majority in the rich river valleys stretching from Baghdad to Basra had begun to claim power and marginalize the Sunnis.
For this reason any movement that promised power to Sunnis in the region was appealing. The Sunni shining knight that appeared on the scene in 2004 was a militant jihadi from Jordan, Abu Musab al-Zarqawi. Born into a refugee Palestinian family, the young Zarqawi turned to a life of drugs and petty theft in his youth, but later underwent a conversion into a strict form of Islam influenced by the rigid moral codes of the Wahhabi form of Islam prominent in Saudi Arabia. Among other things, it allowed for beheading as an acceptable punishment for those who threatened the faith.
The movement he created in Iraq was based on these teachings and on the longing of Sunnis in the western region of the country to be free of both American military occupation and Shi’a political domination. He named his movement al Qaeda in Iraq, hoping to receive support from the international organization headed by Osama bin Laden and Aymen al Zawahiri, at that time hiding out in Pakistan after the U.S,. invasion and occupation of Afghanistan. Relations between Zarqarwi and bin Laden were never good, however, since Zarqawi insisted on his own priorities and his own leadership style. The al Qaeda leaders were uncomfortable with Zaraqawi’s extreme anti-Shi’a stance, and his easy adoption of beheading as an intimidating tactic, which bin Laden and Zawahiri thought would alienate the population.
The al Qaeda leaders were right, and though al Qaeda in Iraq flourished for a time with support from young radical Arab Sunnis especially after the U.S. destruction of the city of Fallujah in 2004, the Sunni tribal elders were increasingly wary of Zarqawi’s authoritarian leadership and his rigid Islamic policies. In 2006 Zarqawi was killed by U.S. military forces. The new head of al Qaeda in Iraq was an Egyptian, Abu Ayyub al Masri, who kept the name of al Qaeda but announced that the organization would be creating an Islamic state in the region, headed by an Iraqi Caliph, Abu Omar al-Baghdadi. Al Masri and al Baghdadi were killed by a U.S. military strike in 2010 and their movement turned to another Iraqi as leader; he took the name of the fallen al Baghdadi, naming himself Abu Bakr al Baghdadi. It is this Baghdadi who later proclaimed himself the Caliph of the Islamic State.
For a time, however, the predecessor organization, al Qaeda in Iraq, was defeated. In 2007 under the leadership of U.S. General David Petraeus, U.S. troops were withdrawn from the Sunni regions of western Iraq and local tribal militias were empowered to turn against al Qaeda in Iraq, which eventually restored the region to traditional tribal and religious leadership control. The operation was dubbed the “Awakening.”
This solution worked well while the U.S. was still the occupying force in Iraq, but when the U.S. military withrew its troops in 2011, the responsibility for maintaining the support of the Sunni tribal leaders fell on the shoulders of al Maliki and the Shi’a dominated government in Baghdad. Alas, al Maliki abandoned the Arab Sunni leaders, choosing to shore up his political support largely from his own Shi’a base by using government funding and positions as payouts to his political supporters. Once again, the Arab Sunnis regarded themselves as marginal and disenfranchised.
This is where al Baghdadi and his Islamic State came back into the picture. The uprising in neighboring Syria that began in 2011 gave him a nearby base of operations as his cadres infiltrated the resistence fighters and built their own jihad army, eventually controlling large sections of Sunni Arab dominated sections of eastern Syria. Their main competition in that battle weary country was another movement affiliated with al Qaeda, the al Nusra Front, with which the al Qaeda leader, Zawahiri, urged al Baghdadi to collaborate. Al Baghdadi was determined to go his own way, however, rejecting al Nusra and the name “al Qaeda,” and proclaiming an Islamic State. In 2014 the movement roared over the borders between Syria and Iraq, and even conquering Iraq’s second largest city, Mosul, which it plundered for its wealth and military armament.
The complicity of the Sunni Arab population in the ISIS administration in Syria and Iraq has been largely opportunistic, not ideological. When I interviewed villagers in 2015 in Iraq’s Kurdisan who had fled ISIS control they told me that the only people in their villages who supported ISIS did so for opportunistic political and economic reasons. These Sunnis and their tribal leaders could as easily turn against ISIS as they have supported it, if they were given other options for participation in public life. This is what happened during the Awakening movement, and al Baghdadi remembers how fickle the Sunni followers were in abandoning al Qaeda in Iraq at that time. For this reason he has instituted a reign of terror in ISIS controlled areas to intimidate the Sunni populace into compliance.
It’s fair to describe ISIS as a terrorist regime, since it uses extreme acts of violence to intimidate both its enemies and its own population. The savage beheadings of Western journalists and aid workers that were posted on the Internet were matched by dozens, perhaps hundreds, of beheadings of recalcitrant Sunnis under ISIS’ control who refused to go along with its demands or who dared to be identified as Christians, Yazidis and other minorities—or even as modern people who liked to dress in a Western style. For ISIS, terror has been an instrument of governance.
But even terror can go only so far in controlling people against their will. So when cities such as Ramadi and Fallujah are liberated, most of the population is relieved to see ISIS go. They are not, however, necessarily pleased to see a Shi’a based government take charge, or to subject themselves to marauding bands of Shi’a militia. Hence the long-range future of eastern Syria and western Iraq is open to question. I see three possibilities for resolving the dilemma of Sunni empowerment:
Integration: Return to Syria and Iraq.
The governments of Syria and Iraq could exert massive control over the region after the fall of ISIS and forcefully reintegrate eastern Syria into Syria and western Iraq into Iraq. The degree to which the Sunni population will be acquiescent to this reintegration depends on two things: whether the governments in Damascus and Baghdad will be able to force their control on the region, and whether they will be willing and able to change their Shi’a – dominant power structure and allow full Sunni participation in public life. Ideally they would have the wisdom to open up their government to more Sunni involvement which would lessen the resentment of Sunnis about being left out of the governments in both countries.
There is some indication that the Iraq government recognizes that it has to include Sunnis in leadership roles, especially in those areas of western Iraq that are Sunni majority. The invasion strategy undertaken by the Iraq government in Ramadi and Fallujah recognized the problem of Sunni resentment, and in both places the forces that were the vanguard in liberating the inner cities were Sunni tribal militia. In the case of Ramadi, the Sunni tribal leaders were involved in reconstructing the political infrastructure of the city, and although they have quarreled with one another, they have at least provided the impression of Sunni leadership rather than Shi’a occupation of their city. Whether this support for Sunni leadership will continue in ISIS-liberated areas remains to be seen.
Alas, however, both the Iraqi and Syrian governments seem to have resisted any suggestion of change or power-sharing, even as the Sunni resistance has mounted. When early in 2016, Haider al Abadi, Iraq’s Prime Minister, suggested that constitutional reforms should be considered to allow for greater Sunni participation, the government’s headquarters in Baghdad’s Green Zone were invaded by Shi’a militia loyal to the firebrand anti-Sunni cleric, Muqtada al Sadr, where Muqtada’s supporters staged a protest in the Iraq parliament, temporarily shutting it down. As the riots by Muqtada al-Sadr’s militia show, there is huge Shi’a pressure against any attempt to restructure the government to be more open to Sunnis.
In Syria, Bashar al Assad has been similarly intransigent, ignoring the plans presented by United Nations envoys for power-sharing governmental change that might have prevented much of the ethnic strife within his country. Instead he has doubled down on the resistance against what he regards as simply terrorism. Iran could play a key role, however, in changing the minds of leaders in both Damascus and Baghdad. So could Russia, in the case of Syria; the US still has some influence in Iraq. Whether these global powers will be exert their influence to try to find a long-range solution to the integration of Sunnis within Syrian and Iraqi political society remains to be scene. Without a solution, insurgent movements such as ISIS will continue to find a safe haven in the region.
Separation: The Emergence of Sunnistan.
A more radical solution would be the creation of a separate state. The contiguous areas of eastern Syria and western Iraq currently controlled by ISIS do indeed demarcate a cohesive ethnic region which had some autonomy in the Ottoman period and could again be a separate political entity. Since Kurdistan in northern Iraq is already de facto a separate state, there is already a move towards the disintegration of Iraq. When I arrived at the airport in Erbil in 2015, for instance, I saw large banners that said “Welcome to Kurdistan” with no mention of Iraq; while I was there I had dinner with a member of the Kurdistan “foreign ministry,” as they called it, although it is officially the office of external affairs of the regional government of Iraq. So in a similar way, Fallujah could become the gateway to Sunnistan.
It is conceivable, however, that a Shi’a government in Baghdad would be relieved to be free from the headaches of western Iraq, especially if there were security guarantees and financial incentives for doing so. It is also possible to see Assad being pressured into shuffling off the eastern region of Syria that has caused such headaches for him as long as he could reassert control over the rich and populous western region. At the same time, elites within the countries want to maintain united control, and there is also pressure from outside against any fragmentation of the two countries. This pressure comes in part from the United States and neighboring states in the Middle East that fear the possible devolution of power if separation ensues. So it’s not clear whether this scenario would get official sanction from either Damascus or Bahgdad.
Dissolution: Sunni Control in the Failed States.
But a kind of unravelling may occur whether it is officially sanctioned or not. Both Syria and Iraq exhibit some aspect of failed states—an inability to maintain control much beyond their capitals and centers of support. If they are able to uproot ISIS and not dramatically change the politics of the Sunni regions and gain their voluntary support—or if neither Damascus nor Baghdad maintains sufficient strength to force compliance—then de facto control will revert to Sunni tribal leadership. This is the most likely scenario, the result of doing nothing. In the Sunni heartland of Eastern Syria and Western Iraq, the Sunni tribal leaders will continue to maintain order, however, the way they always have done. There will be a de facto Sunnistan though not one officially proclaimed.
ISIS as a Global Jihadi Movement
But ISIS is more than territory, and more than a Sunni Arab enterprise. Al Baghdadi’s strategy of recruiting young people from around the world to participate in a glorious struggle has succeeded perhaps far beyond his expectations. The ISIS-related attackers in San Bernardino were from Saudi Arabia; the Paris nightclub and Brussels airport bombers were Belgian of Moroccan descent; the Orlando shooter was an American of Afghan descent; the attackers at the Istanbul airport in June 2016 were from Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan and Dagestan. None were Syrian or Iraqi, the areas where ISIS has its territorial base, yet in those areas foreigners from around the world have come to join the Caliphate’s army. “They are all foreigners,” one refugee told me in describing the ISIS soldiers who captured his village in northern Iraq.
This far flung network is maintained through Internet communication, through Twitter and closed websites, and through glossy online magazines such as Dabiq that amounts to something of a Cyber Caliphate. The young people who were lured to this network and who maintain it came with a variety of motives. Perhaps the strongest was the desire to be involved in a great war, a cosmic struggle that allowed them to play out all of their computer game fantasies of warcraft, valor and gore. But some also came out of a sense of history and piety, a conviction that they were laying their lives on the line for something of transcendent importance for Islamic civilization.
Some of the young volunteers from around the world were attracted to the dramatic vision of apocalyptic cosmic war that animated the inner circle of the movement; others also joined the movement to gain a sense of identity and to be a part of a community. For young people of Middle Eastern parentage who were living in the UK, Europe, and the United States, their experience of being alienated and marginalized immigrant youth was overcome by the acceptance offered by ISIS. Initially their main form of participation was through online chat rooms and Twitter feeds.
My own student research assistants have monitored these Twitter accounts and found that the conversation was dominated by a sense of the importance of the cause, and the sharp we-they distinction between members of the movement’s community and all outsiders, whether or not they were Muslim. A Canadian research scholar, Amarnath Amarsingam, who has interacted with many young Canadian volunteers on Twitter, concurs that community is a dominant part of the appeal. Many of the Twitter called themselves members of the Baqiyah family, using the Arabic term for “enduring” that ISIS employed as one of hallmarks.
“Trust me, I’ve never felt like I’ve belonged anywhere until I met the brothers and sisters on line,” one young volunteer told Amarsingam. “The Internet keeps us connected, keeps us a family,” he added. Then Amarsingam asked the young man to say more about the sense of belonging he felt in the Baqiyah family, and he responded saying that he felt more authentic as a person within the Internet community: “sometimes it’s like the person on line is the real you.” Another Canadian research scholar, Marc-André Argentino, who has also been monitoring ISIS-related Twitter accounts, agrees with Charlie Winter’s analysis of the “Virtual Caliphate” that the category of “belonging” is one of the most important themes. “Regularly,” Argentino reports, “images and video are published depicting brothers praying together and eating together, listening to sermons online, of brothers in arms hugging each other after combat operations, or huddled together hands in the middle (an image reminiscent of a sports team).” The pictures show the ISIS brotherhood together in physical space, but the sense of community appears to be almost as strong in the connections provided through the media of cyberspace.
For this reason, the cyber community of ISIS will likely persist long after the physical control of territory in Syria and Iraq have been abandoned. The digital apparatus of websites, cybermagazines, video uploads, Twitter communications and dark web locations has been well established and though it may be interrupted by ISIS’ territorial defeat, it likely will be maintained in some form somewhere in the world other than in the ISIS controlled cities of Raqqa and Mosul. There is no reason to think that they will be entirely dismantled.
Indeed, the passion of belonging to the ISIS cyber community might even intensify in the period after the fall of territorial control. Perhaps nothing brings together a community as the sense of being under siege and needing to band together for strength. The Twitter feeds in mid-2016, for instance, were buzzing with the assaults on Fallujah, Raqqa and Mosul, with rallying cries to defend the Caliphate.
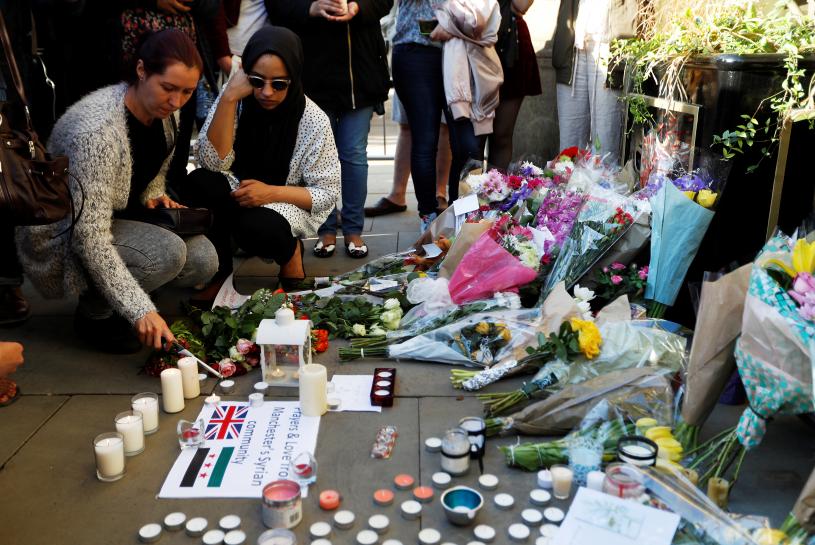
One of the strategies employed by ISIS was to use terrorist attacks against the far enemies of the movement—the countries of the United States, France, Turkey and elsewhere that it regarded as being in league with those local forces that were trying to defeat the Islamic State. For this reason, messages went out early in 2016 for young followers around the world to undertake terrorist actions on their own wherever they were. An ISIS spokesman, Abu Mohammad al-Adnani, urged followers around the world to make the month of Ramadan in 2016 “a month of calamity everywhere.” Individuals were told that they did not need to check with ISIS headquarters in Raqqa but attack unbelievers in the name of ISIS wherever they were.
The attacks by ISIS sympathizers in Paris, Brussels and Istanbul certainly seemed to be well coordinated multiple attacks of the sort that the ISIS central command would support and perhaps even help to plan. Attacks in the American cities of San Bernardino and Orlando appear to be less well organized, conducted by one or two people inspired by ISIS ideology. The perpetrator of the Orlando attack, Omar Mateen, did exactly this—he declared his allegiance to the head of ISIS, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, by telephone to 911 emergency operators minutes into his rampage. He was said to have been surfing ISIS sites on line in the weeks before the attack. And the ISIS news agency quickly proclaimed him a “fighter for ISIS.”
The term “ISIS inspired,” however, might not be quite fitting for the Orlando attack, and for some of the others as well, since “ISIS inspired” implies motives that were primarily related to an allegiance to the ideology of the Islamic State. It also implies that the primarily intention of undertaking an act of terrorism is to carry out the broad directive of movement—in this case attacking unbelievers and enemies of the ISIS cause. There is some evidence that the perpetrator of the Orlando attacks, Omar Mateen, also had personal motivates, and attacked a gay bar out of a homophobic rage. In this case, what we can say is that is acts were “ISIS branded,” both by Mateen and by the ISIS leadership, whether or not it was directly inspired by ISIS ideology.
This may be part of the dark future of the ISIS global jihadi network. The encouragement of ISIS for individuals to take up bombs against secular and non-supportive Muslim societies leaves room for a plethora of acts of terrorism undertaken for mixed motives but given the legitimization of ISIS ideology through ISIS-branding. Individuals can be comforted by the fact that even though their horrible actions are condemned by most people, including most Muslims, around the globe, their comrades in the online communities forged through Internet connections will digitally applaud their crimes.
ISIS as an Apocalyptic Cult
The reason why some of the foreign fighters are so passionate about the ISIS enterprise is that they are convinced that it is at the leading edge of a cosmic battle between good and evil that will usher in the last days of the planet and signal the arrival of the Islamic savior, the Mahdi. Though only some of the fighters are propelled by this belief, and few of the ordinary Sunnis in ISIS-controlled territory share it, this is a dominant motive of the inner circle of the movement.
This “ISIS apocalypse,” as William McCants describes it in a perceptive book with that title, is a kind of extreme variant of Wahhabi Muslim apocalyptic thinking. Soon after the fiery leader of al Qaeda in Iraq, Abu Musab al- Zarqawi, was killed in 2006, his successor, Abu Ayyad al-Masri, turned to apocalyptic thinking to characterize the movement as the Caliphate that would emerge at the end times. He thought that the Mahdi would be coming soon and that the faithful had to act quickly to establish a Caliphate to receive him. His successor and self-proclaimed Caliph of the Islamic State, Abu Bakr al Baghdadi, shared that view. The name of the ISIS online magazine, Dabiq, refers to a town in northern Syria that was the location of the battle of Marj Dabiq between the Ottoman Empire and the Mamluk Sultanate in 1516. It is an ISIS belief that this town will be the location of the final battle between true believers and infidels that will usher in the apocalypse.
The strict code of behavior and extreme brutality in dealing with perceived enemies are aspects of the ISIS movement are grounded in some instances of medieval Islamic history and practice. The relation between this kind of reign of terror and religion is problematic, however. One can claim that the ISIS policies are vicious because their religious understanding requires the faithful to act this way, or one can say that their need for an intimidating form of extreme violence needs to be justified, and they have found recourse in ancient tradition to do so. Either way it is an eerie relationship between religion and extreme violence.
Many have challenged whether ISIS should be called Islamic. Muslims around the world have risen up to protest against what they describe as the non-Muslim attitudes and actions of ISIS. Iyad Ameen Madani, the Secretary General of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation, a group that represents 57 countries and 1.4 billion Muslims, said ISIS “has nothing to do with Islam and its principles.” Similar denunciations have come from leading Muslim clergy in Egypt, Turkey, and around the world. Still, the leaders of ISIS claim Muslim authority for their actions, strict Shari’a law as the basis of their jurisprudence, and the promise of salvation for those recruited into its ranks.
The religious credentials of al Baghdadi gives some credibility to this religious appeal. He is a cleric whose family can claim ancestry to the family of the Prophet. He received a PhD in Islamic Studies from the Islamic University of Baghdad and knows the scriptures and the tradition of Islam better than most jihadists. Osama bin Laden had no religious credentials, and though he pretended to be an engineer, his college training was in business management; Ayman al Zawahiri was a medical doctor; and al Baghdadi’s predecessor in leading al Qaeda in Iraq, Abu Musab al Zarqawi, was a street thug from Jordan. By contrast, al Baghdadi looks fairly legitimate. His credentials do not make the movement Islamic, however. Nor do the Islamic whitewashing of the regime’s terrorist actions and cruel restrictions make them Muslim. The judgment is in the eye of the beholder. And to most Muslims, ISIS represents the antipathy of the faith.
Still, every religious tradition has its peculiar extremists. Often these are marginal cults that communicate largely among themselves and do not surface to public attention unless they are involved in some kind of bizarre behavior. The Heaven’s Gate cult in the United States, for instance, believed that they would be taken up into outer space by UFOs in the last days of the world, a prophecy that was ignored by most people until they committed mass suicide in an attempt to collectively hasten their salvation. Similarly, it is quite possible that the apocalyptic ideas of ISIS will live on in small cults that cherish their ideas but do not have the means nor the need to force them on others in a violent way.
Transformation of Cosmic War
The key question in the transformation of the inner circle of true believers in the ISIS apocalyptic ideas from a terrorist regime to a benign cult is whether the image of cosmic war can be contained. Every religious tradition has such images of dramatic existential battle between the forces of good and evil, order and chaos. They have been a part of virtually every religious tradition from early times to the present. The sacred writings of the Hebrew Bible, the Qur’an and the Hindu epics are rife with them, and the histories of Sikhism and Theravada Buddhism abound in glorified warfare for religious purposes. Yet for most believers in Christianity, Judaism, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism and Sikhism, these images of warfare are symbolic and metaphorical. For most Muslims, the true jihad is the battle between good and evil within one’s own soul.
But once these images of cosmic war are applied to real situations of territorial struggle and guerilla warfare can they ever be put back in the metaphorical box? The history of extreme movements, such as the Khalistani movement of Sikhs in northern India that erupted into violence in the 1980s and then became quiescent, shows that it is possible. At the same time, some people within the movements will be convinced that the battles have to be conducted in real time and space in order to be a legitimate form of the cosmic war in which they believe. They will continue to plot schemes of attack, and occasionally conduct them in sporadic, uncoordinated terrorist assaults.
Hence ISIS may end. It may lose its territorial control, and it may not be able to manage the entire communications infrastructure that made it for a time such an imposing force around the world. But aspects of it may remain in forms of Sunni empowerment and in small cells of true believers. For the most part these may be benign. But as recently history has aptly demonstrated, it does not take many activists with an extreme agenda and a willingness to lose their own lives in suicide assaults to do a horrendous degree of damage. Thus the specter of ISIS may continue to haunt the world for some time to come.
Research support for this project has come from the Resolving Jihadist Conflicts Project of the department of Peace and Conflict Resolution Research at Uppsala University in Sweden. I appreciate the help from my research assistants, Saba Sadri and Mufid Taha, and from the Pacifica Institute for arrangements assistance in the Kurdistan region of Iraq.